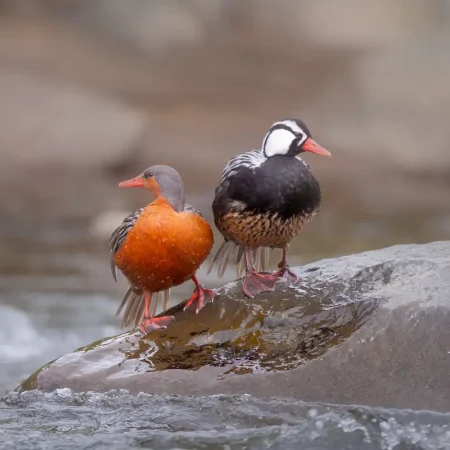
Torrent Duck Project


Context and objectives
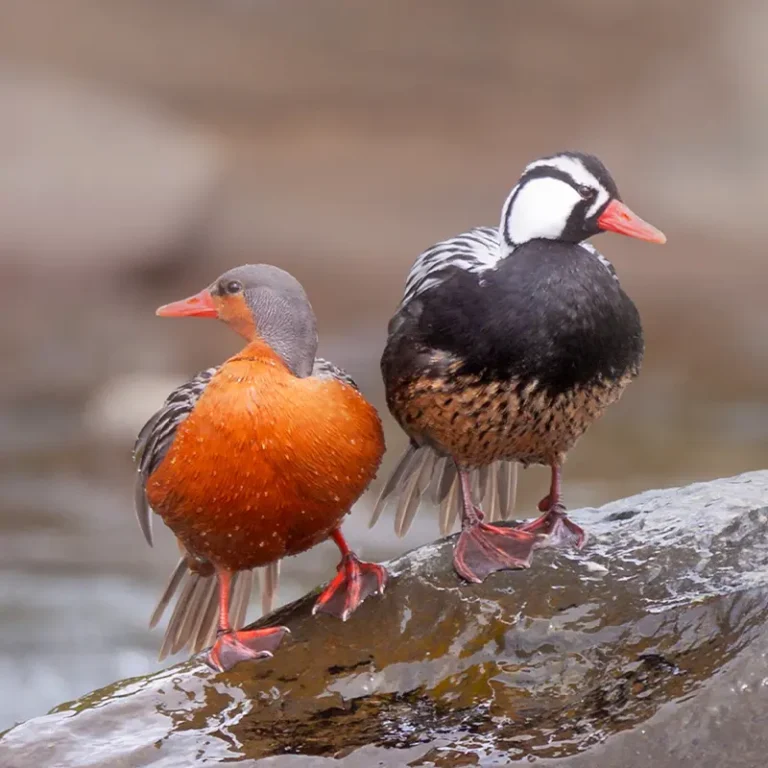
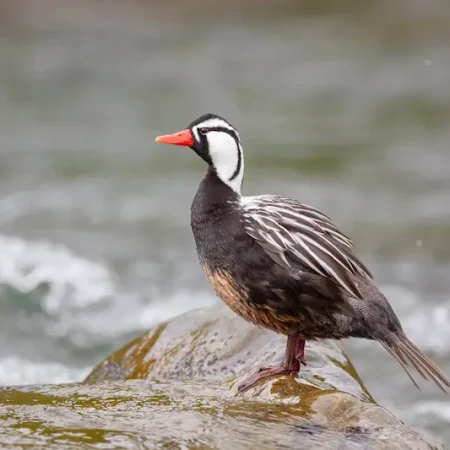
The Torrent Duck is a charismatic species throughout its distribution, but especially so in Southern Patagonia, as it inhabits areas of great scenic interest and with a lot of recreational use. But also, because it is in Patagonia where the population reduction of the Torrent Duck is very striking, with very striking local extinctions. The discussion about the growing rarity of the species has led numerous researchers and specialists from institutions linked to conservation to focus on some of the problems, mainly “chasing” human recreational activities, but without really solid evidence, and at the same time abandoning or underestimating the impact of other threats, such as invasive species.
Surely the threats act synergistically, even more so in a context of climate change. That is why we have set out to learn about important aspects of the species’ ecology, the real impact of the threats, but also to develop management plans that allow us to recover their populations.
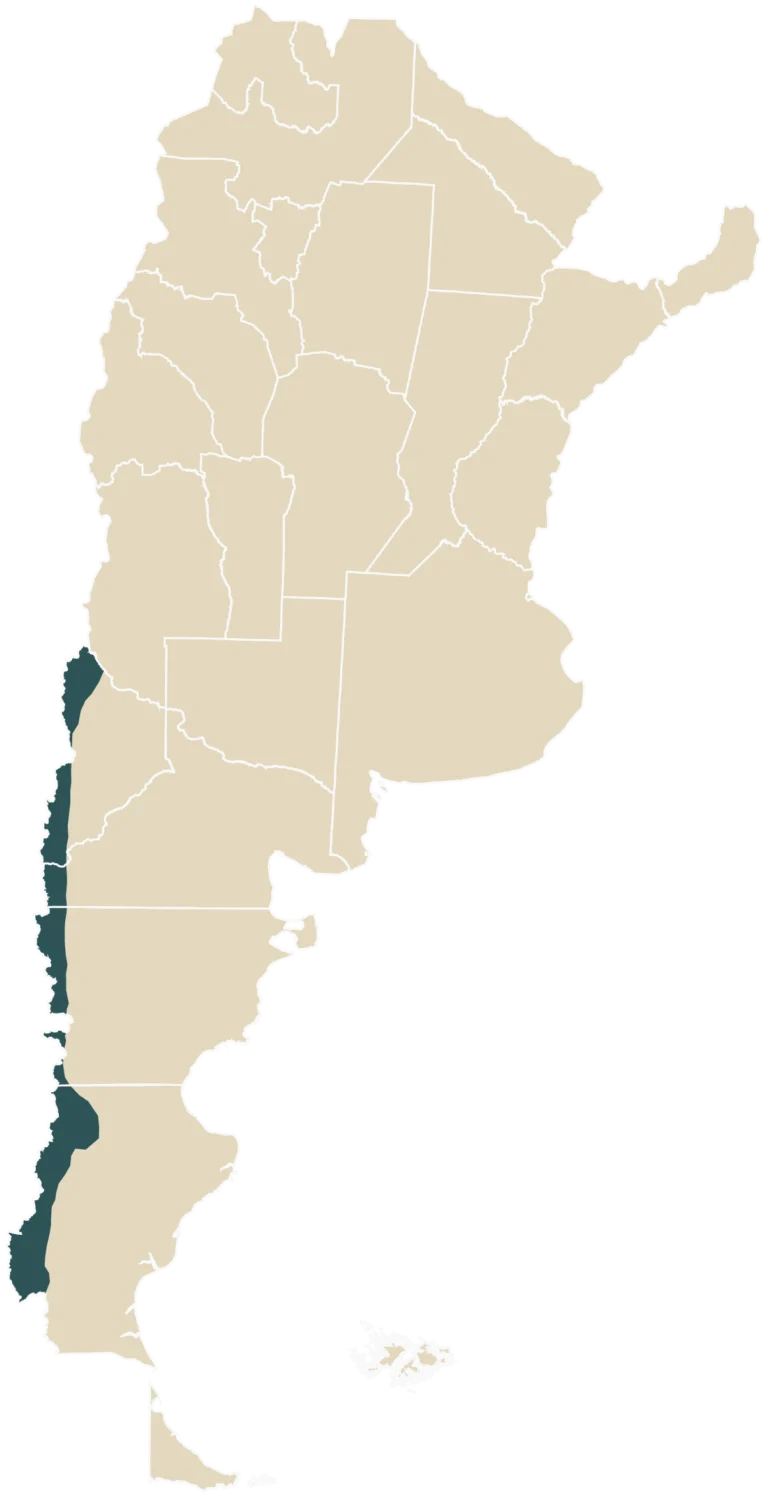

Scope of the project
Our actions
- Population monitoring of its entire distribution area.
- Monitoring the progress of its main threats -invasive species and recreational and urban human use-.
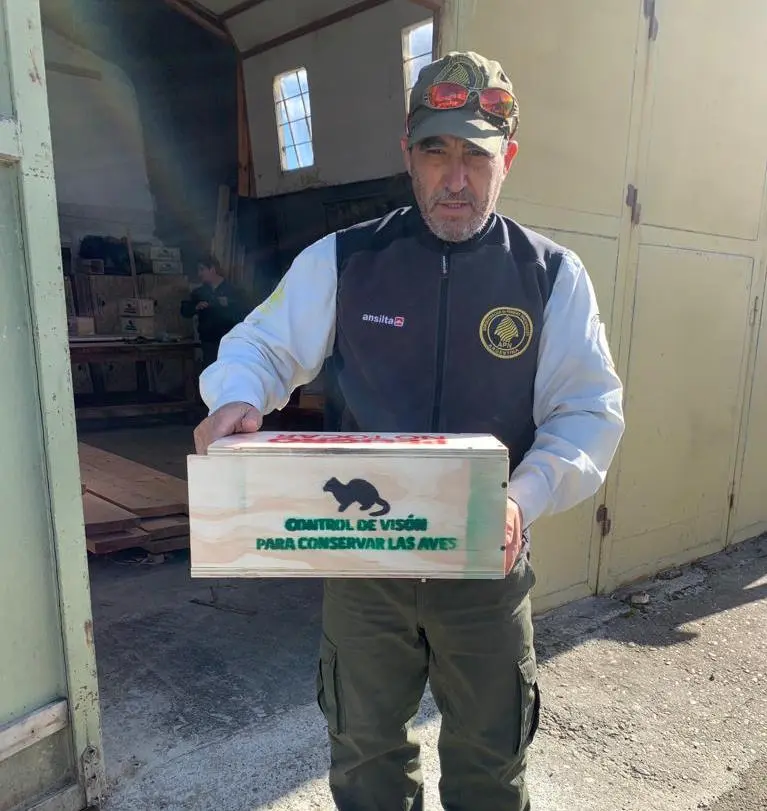
- Protection of populations through the control of invasive species -American Mink-. Studies on ecology, demography, and conservation.
Protagonists
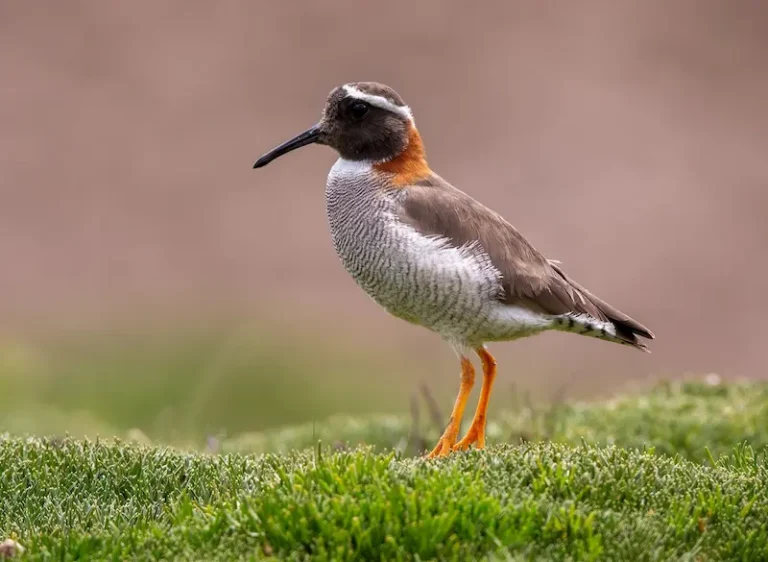
Habitat and behavior
They inhabit fast-flowing watercourses of the Andes, from Tierra del Fuego to Venezuela. In Argentina, two races inhabit, one in Cuyo and Patagonia and the other in the Northwest. They live in pairs and tend to maintain the same territory. They have adaptations for the extreme environment where they live, such as large legs, developed musculature, hydrodynamic body, and a long, rigid tail that serves as a rudder.
Feeding
They scrape submerged rocks in fast-flowing rivers to obtain larvae of benthic macroinvertebrates (e.g. insect larvae, such as mayflies).
Reproduction
For pair formation, males compete by showing off in front of the female. They nest in high places on the river bank. The nest may be in the hollow of a tree or on a rock ledge. The eggs are large, incubation is carried out by the female (up to 44 days!), the longest among ducks.
Curiosity
To feed, it dives in the strong currents and uses a conical and flexible beak, unique among anatidae, which allows it to scrape the rocks to obtain its food.
Threats
Human alterations and climate change are considered the main threats. Invasive species were also mentioned as a problem. However, we believe that the latter have been underestimated.

































